Bases to Uric Acid
Bases to Uric acid
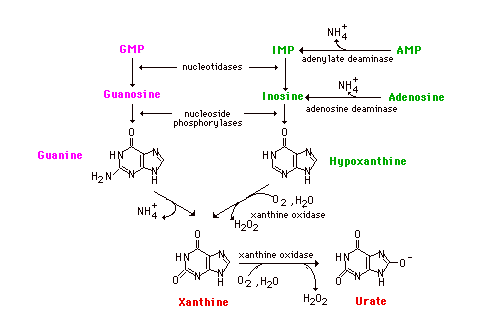
Bases to Uric Acid compose of Both adenine and guanine nucleotides converge at the common intermediate xanthine. Hypoxanthine, representing the original adenine, is oxidized to xanthine by the enzyme xanthine oxidase. Guanine is deaminated, with the amino group released as ammonia, to xanthine. If this process is occurring in tissues other than liver, most of the ammonia will be transported to the liver as glutamine for ultimate excretion as urea.
Xanthine, like hypoxanthine, is oxidized by oxygen and xanthine oxidase with the production of hydrogen peroxide. In man, the urate is excreted and the hydrogen peroxide is degraded by catalase. Xanthine oxidase is present in significant concentration only in liver and intestine. The pathway to the nucleosides, possibly to the free bases, is present in many tissues.
Purine and pyrimidines from tissue turnover which are not salvaged are catabolized and excreted. Little dietary purine is used and that which is absorbed is largely catabolized as well. Catabolism of purines and pyrimidines occurs in a less useful fashion than did the catabolism of amino acids in that we do not derive any significant amount of energy from the catabolism of purines and pyrimidines. Pyrimidine catabolism, however, does produce beta-alanine, and the endproduct of purine catabolism, which is uric acid in man, may serve as a scavenger of reactive oxygen species.
The end product of purine catabolism in man is uric acid. Other mammals
have the enzyme urate oxidase and excrete the more soluble allantoin as
the end product. Man does not have this enzyme so urate is the end
product for us. Uric acid is formed primarily in the liver and excreted
by the kidney into the urine.
Reprint Permission Given to Gout-Aware All Articles written & supplied by
Dr Carol .N. Angsatdt Ph.D Department of Biomedical Sciences Allegheny University of Health Sciences
For further studies, you could get a Uric acid test done, by measuring the amount of uric acid in the urine.
A uric acid test measures the amount of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is a chemical that’s produced when your body breaks down purines. Purines are chemicals that enter the bloodstream during the natural breakdown of cells in the body. They’re also created during the digestion of certain foods, such as:
- anchovies
- sardines
- mushrooms
- mackerel
- peas
- liver
Once purines release uric acid. Most of it’s dissolved in the blood and transported to the kidneys, where it’s removed from the body through urination. Some uric acid also leaves the body through defecation. When this process is disrupted, however, your body can produce too much or too little uric acid.

Recent Articles
-
Tony
May 08, 24 08:57 PM
Hi Peter, I am a physician, had my first Gout episode last week. I was surfing through the web and happened to come across your site. I am impressed by -
What is it about Cherries?
Aug 25, 21 03:59 AM
Allopurinol worked for me, but at the expense of adversely affecting my mood.I like cherries, but getting them every day of the year is a problem.I wondered -
ACV made my gout worse...
Apr 22, 20 07:19 AM
During my first gout attack, I was in so much pain that I desperately scoured the internet for alternative cures as the colchicine that I was prescribed


