Purine Catabolism
Nucleotides to Bases
Guanine nucleotides are hydrolyzed to the nucleoside guanosine which undergoes phosphorolysis to guanine and ribose 1-P. Man's intracellular nucleotidases are not very active toward AMP, however. Rather, AMP is deaminated by the enzyme adenylate (AMP) deaminase to IMP. In the catobilsm of purine nucleotides, IMP is further degraded by hydrolysis with nucleotidase to inosine and then phosphorolysis to hypoxanthine.
Purine Catabolism
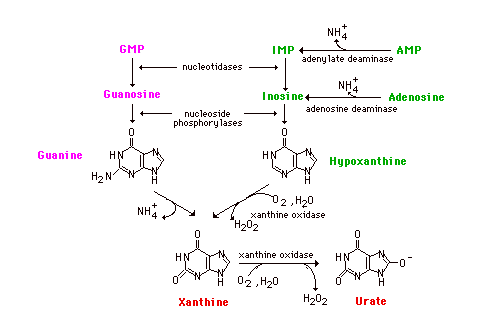
Adenosine does occur but usually arises from S-Adenosylmethionine during the course of transmethylation reactions. Adenosine is deaminated to inosine by an adenosine deaminase. Deficiencies in either adenosine deaminase or in the purine nucleoside phosphorylase lead to two different immunodeficiency diseases by mechanisms that are not clearly understood. With adenosine deaminase deficiency, both T and B-cell immunity is affected. The phosphorylase deficiency affects the T cells but B cells are normal. In September, 1990, a 4 year old girl was treated for adenosine deaminase deficiency by genetically engineering her cells to incorporate the gene. The treatment,so far, seems to be successful.
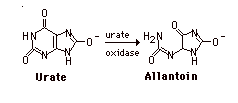
Whether or not methylated purines are catabolized depends upon the location of the methyl group. If the methyl is on an -NH2, it is removed along with the -NH2 and the core is metabolized in the usual fashion. If the methyl is on a ring nitrogen, the compound is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Purine Catabolism Reprint Permission Given to Gout-Aware All Articles written & supplied by
Dr Carol .N. Angsatdt Ph.D Department of Biomedical Sciences Allegheny University of Health Sciences Purine Catabolism

Recent Articles
-
Tony
May 08, 24 08:57 PM
Hi Peter, I am a physician, had my first Gout episode last week. I was surfing through the web and happened to come across your site. I am impressed by -
What is it about Cherries?
Aug 25, 21 03:59 AM
Allopurinol worked for me, but at the expense of adversely affecting my mood.I like cherries, but getting them every day of the year is a problem.I wondered -
ACV made my gout worse...
Apr 22, 20 07:19 AM
During my first gout attack, I was in so much pain that I desperately scoured the internet for alternative cures as the colchicine that I was prescribed







